

The following calculators compute various base and per unit quantities commonly used in the per unit system of analysis by power system engineers.
Calculator-1
Known variables: Base Three Phase Power, Base Line-to-Line Voltage
Formulas and Variables
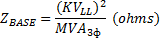
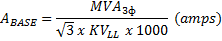
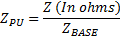
Change of Base Formula

Capacitor Bank Per-Unit Calculations
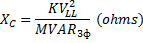
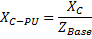
Motor Per-Unit Calculations
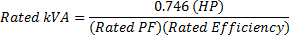
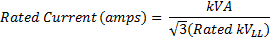
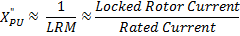
Where:
| ZBASE = Base Impedance |
| KVLL = Base Voltage (Kilo Volts Line-to-Line) |
| MVA3Ф = Base Power |
| ABASE = Base Amps |
| ZPU = Per Unit Impedance |
| ZPU GIVEN = Given Per Unit Impedance |
| Z = Impedance of circuit element (i.e. Capacitor, Reactor, Transformer, Cable, etc.) |
| XC = Capacitor Bank Impedance (ohms) |
| XC-PU = Capacitor Bank Per Unit Impedance |
| MVAR3ɸ = Capacitor Bank 3-Phase Rating |
| X" = Motor Sub-Transient Reactance |
| LRM = Locked Rotor Multiplier |
Background
The per unit system of calculation is a method whereby system impedances and quantities are normalized across different voltage levels to a common base. By removing the impact of varying voltages, the necessary calculations are simplified.
To use the per unit method, we normalize all the system impedances (and admittances) within the network under consideration to a common base. These normalized impedances are known as per unit impedances. Any per unit impedance will have the same value on both the primary and secondary of a transformer and is independent of voltage level.
A network of per unit impedances can then be solved using standard network analysis.
There are four base quantities: base MVA, base KV, base ohms, and base amperes. When any two of the four are assigned the other two can be derived. It is common practice to assign study base values to MVA and KV. Base amperes and base ohms are then derived for each of the voltage levels in the system. The MVA assigned may be the MVA rating of one of the predominant pieces of system equipment or a more convenient number such as 10 MVA or 100 MVA. Selection of the latter has some advantage of commonality when many studies are made while the former choice means that the impedance or reactance of at least one significant component will not have to be converted to a new base. The nominal line-to-line system voltages are normally used as the base voltages with 3-phase power being used as base power.